Balance Disorders Tests
Balance Disorders Diagnostics
Accurate diagnosis is essential to determine the most appropriate treatment for balance disorders. At Harley Street ENT, our specialist doctors, audiologists, scientists and practice nurses provide a full range of vestibular and balance tests.
By prior arrangement, many tests can be performed on the same day as your consultation. This allows a comprehensive assessment in a single visit, which is particularly helpful for patients travelling from abroad or from outside London.
Symptoms that may require balance testing
Balance tests may be recommended for patients experiencing dizziness, vertigo, unsteadiness, light‑headedness, nausea, blurred vision, tinnitus or unexplained falls. Symptoms may be constant or episodic and can significantly affect daily activities.
What balance tests help diagnose
Balance and vestibular tests help identify whether symptoms are caused by inner ear disorders, nerve pathway problems, central neurological conditions or issues with sensory integration. Results guide diagnosis and treatment planning.

Vestibular (Balance) Tests
Vestibular balance tests are used to investigate dizziness, imbalance and vertigo. These tests are not painful, though some may cause temporary dizziness. Patients attending alone may need to rest briefly after testing.
To ensure accurate results, you will be asked to stop balance medication, sedatives and alcohol for at least 48 hours before testing. Please avoid heavy meals and do not wear eye makeup, as this can interfere with camera goggles.
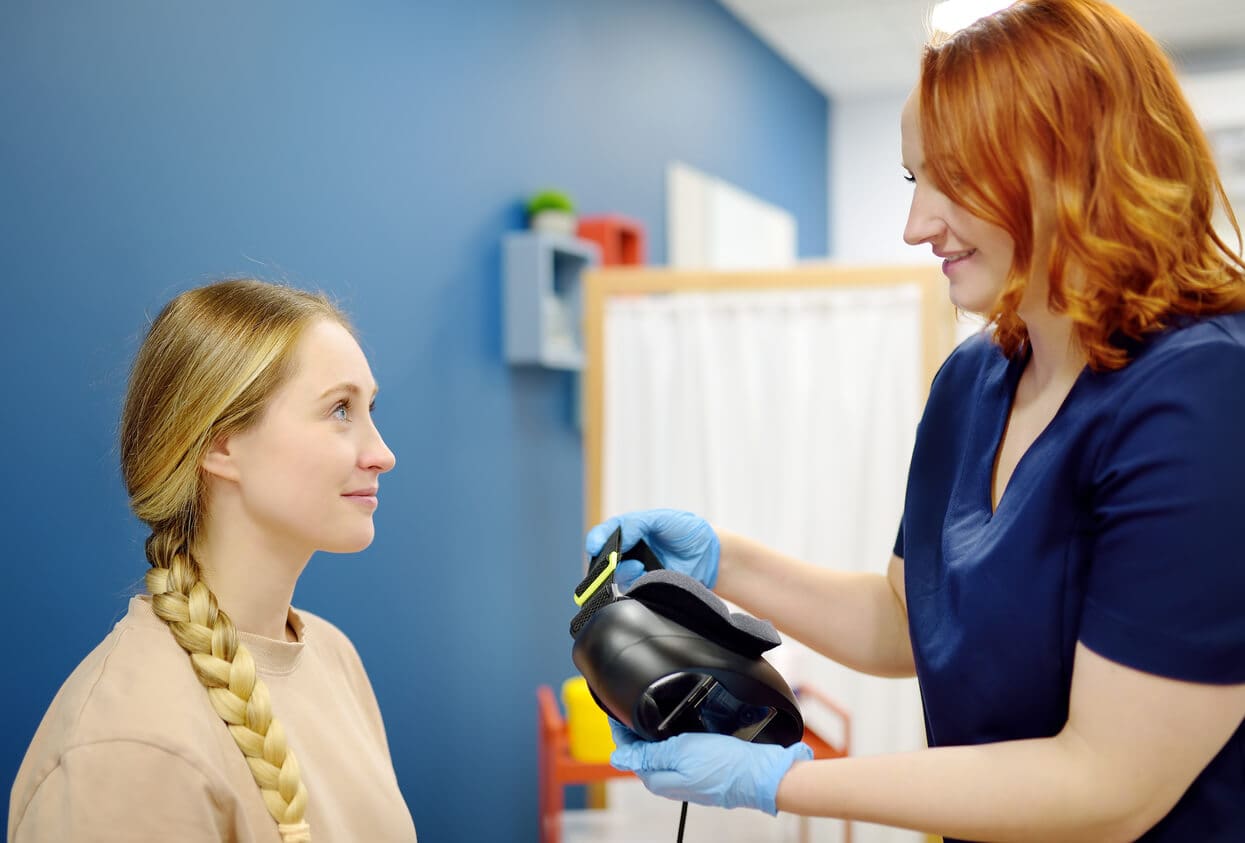

VNG (Videonystagmography)
Videonystagmography analyses eye movements to assess balance function. It helps determine whether balance problems are due to a central (brain) vestibular disorder or a peripheral issue of the inner ear. During the test, you will wear goggles with infrared‑sensitive cameras that record eye movements in a darkened room. You will be asked to focus on a light while your eye responses are recorded digitally for analysis. The test typically takes about 20 minutes.:contentReference[oaicite:1]{index=1}

Calorics
Caloric testing assesses inner ear balance function by gently introducing warm and cool water into the ear canal. This stimulates fluid movement in the balance canals, producing measurable eye movements recorded using infrared goggles.
The test may take up to 45 minutes. Temporary dizziness or nausea can occur but usually settles quickly. Results help identify weakness in one or both inner ears.
Posturography (Sensory Organisation Test)
Posturography assesses overall balance by analysing how visual, proprioceptive and vestibular systems work together. You will stand on a pressure‑sensitive platform while different conditions are applied.
A safety harness is worn throughout the test. Results provide detailed information about balance control and sensory reliance.
VEMP (Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potentials)
VEMP testing checks whether key balance structures and the vestibular nerve are working normally. Sound stimulation of the inner ear causes reflex muscle responses in the neck, recorded via electrodes during the test. This helps identify abnormalities in balance pathways and can detect specific inner ear conditions such as superior semicircular canal dehiscence.:contentReference[oaicite:4]{index=4}
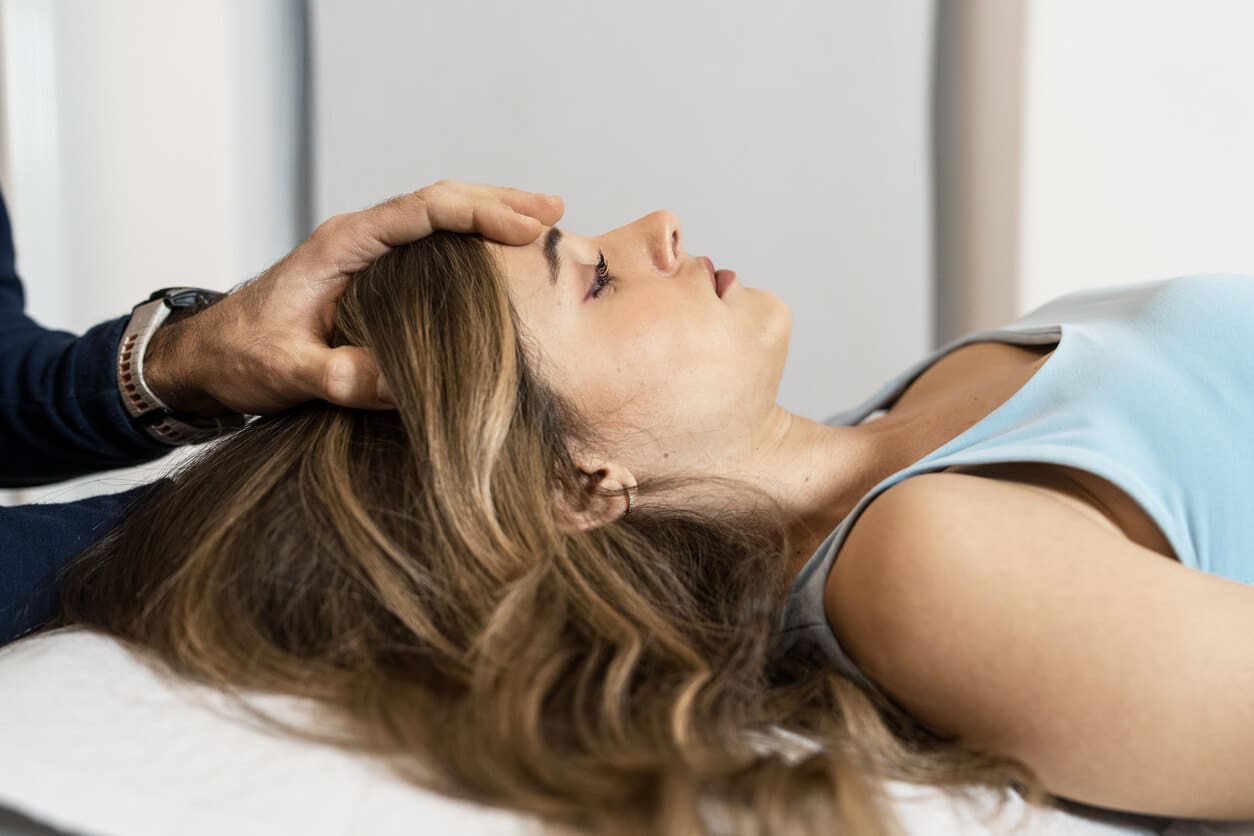

Hallpike Positional Test
The Hallpike positional test is used when benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) is suspected. During the test, your head is moved quickly into specific positions to observe whether particles in the inner ear canals trigger brief episodes of vertigo and characteristic eye movements. This helps confirm BPPV and guide appropriate repositioning treatment.:contentReference[oaicite:5]{index=5}
Fistula Test
The fistula test is performed when there is clinical suspicion of erosion in the bony labyrinth of the inner ear, which may be caused by infection, cholesteatoma or other disorders. Gentle pressure is applied to the ear canal to assess for vertigo or abnormal eye movements, helping to diagnose fistulas affecting balance.:contentReference[oaicite:6]{index=6}

Audiometry
Audiometry forms a core part of balance assessment, as hearing and balance organs are closely linked in the inner ear. A range of hearing tests are used to identify hearing thresholds and middle ear function, providing essential information for diagnosing balance disorders.:contentReference[oaicite:7]{index=7}
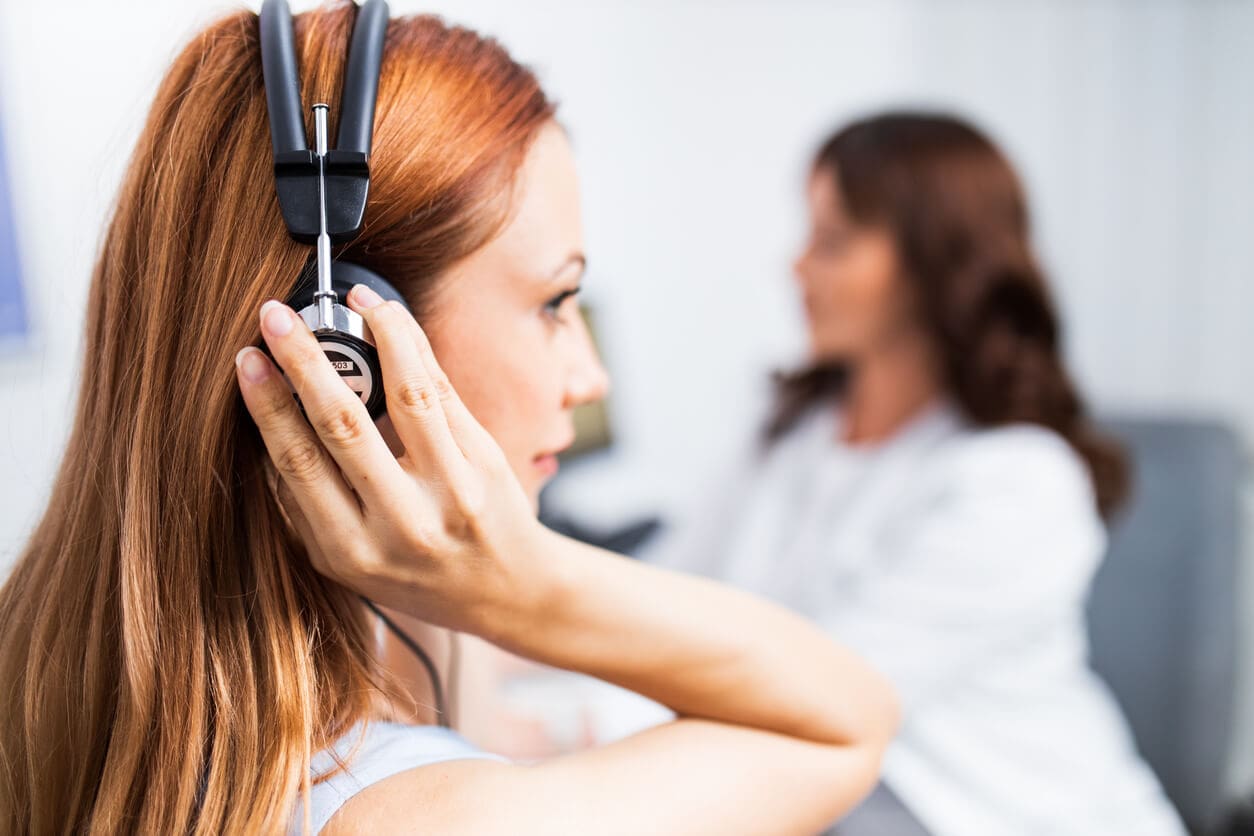
Pure Tone Audiometry (PTA)
Pure tone audiometry determines your ability to hear sounds across different frequencies. You will sit in a soundproof booth wearing headphones and respond to tones at various pitches and volumes. Results help identify the degree and pattern of hearing loss, which supports balance testing and diagnosis.:contentReference[oaicite:8]{index=8}
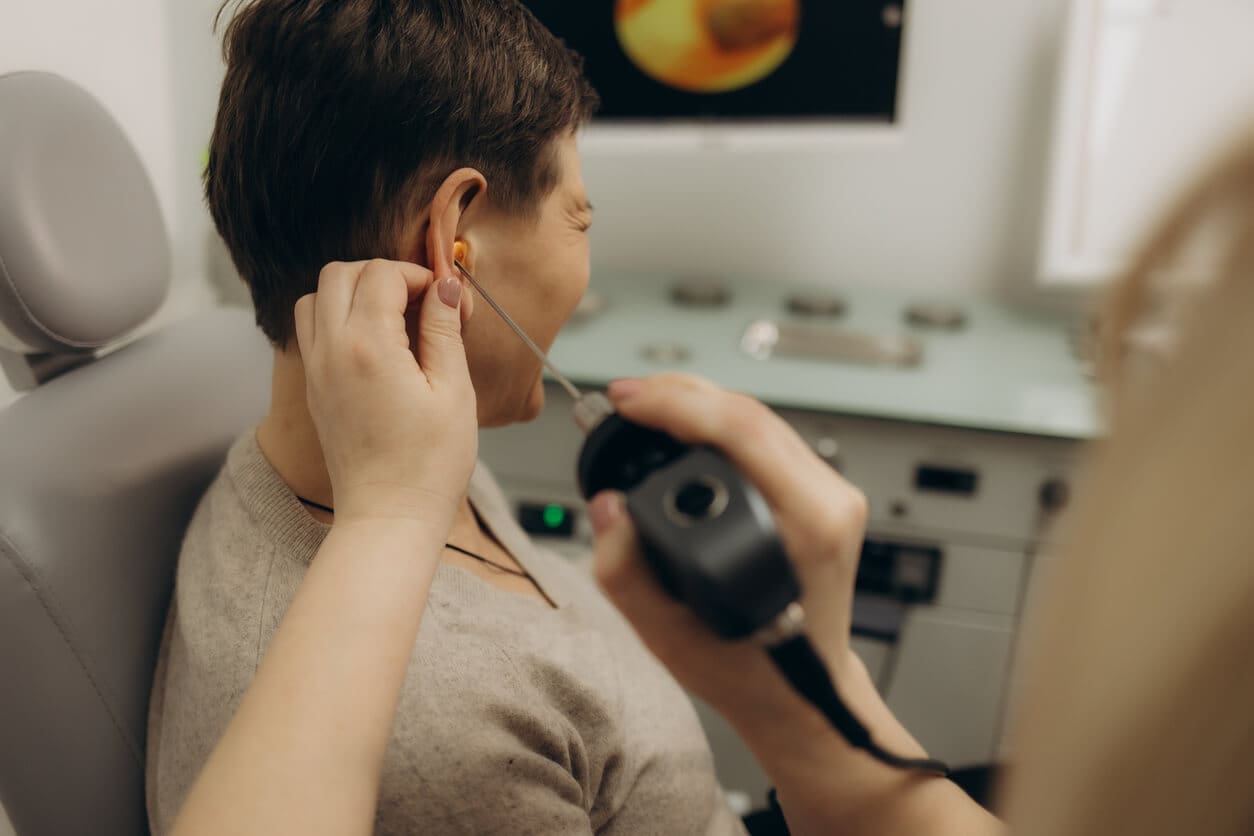
Tympanometry
Tympanometry evaluates middle ear function and can indicate fluid, eardrum perforation, middle ear pressure problems or ossicle dysfunction. During the test, a soft probe is placed at the ear canal entrance, and subtle air pressure changes assess eardrum movement. This helps rule out mechanical causes of dizziness and balance issues.:contentReference[oaicite:9]{index=9}
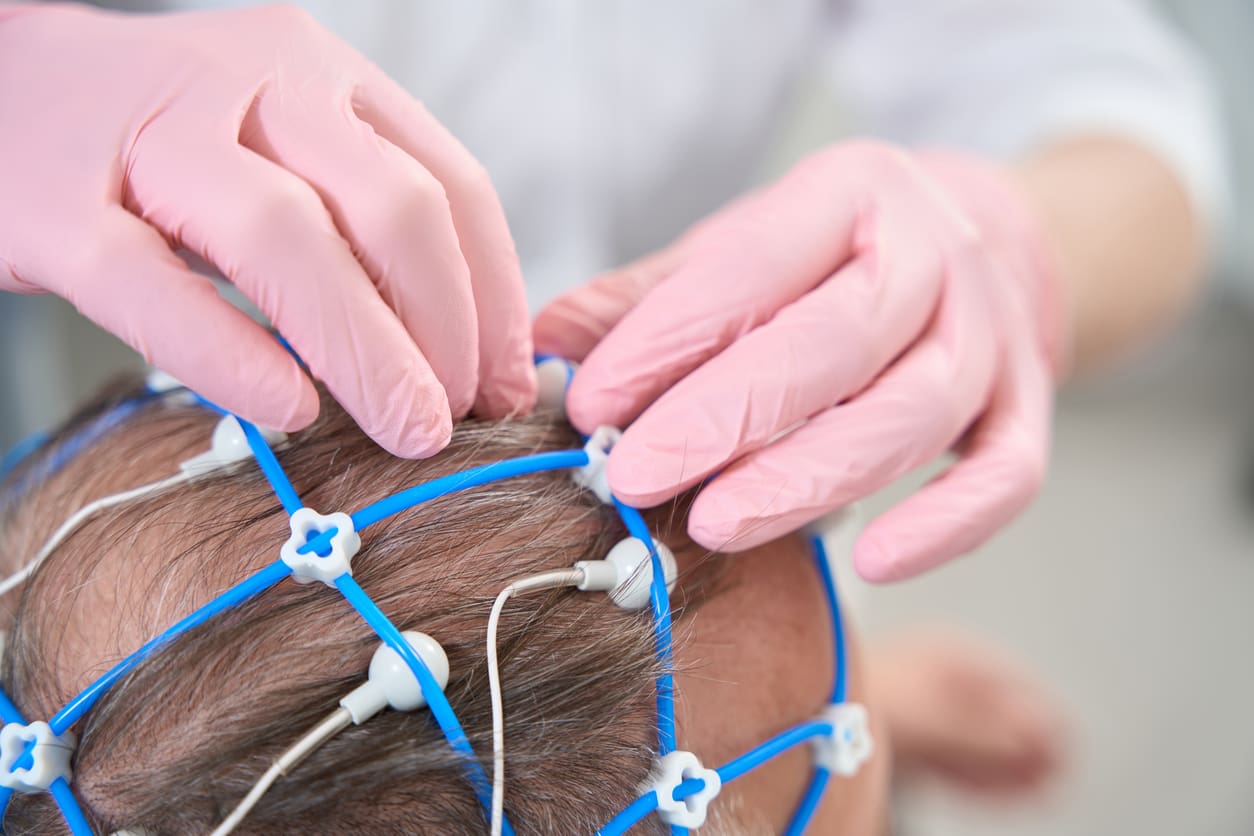
Auditory Brainstem Response (ABR)
Auditory brainstem response testing measures electrical activity along the hearing pathways from the inner ear to the brain. Electrodes placed on the head record responses to sound stimuli, which can help identify neurological or central balance contributions to dizziness and imbalance.:contentReference[oaicite:10]{index=10}
Electrocochleography (EcoG)
Electrocochleography measures electrical potentials in the cochlea and auditory nerve in response to sound. As cochlear fluid pressure changes mirror labyrinth fluid dynamics, EcoG provides objective diagnostic information in conditions affecting balance, such as Ménière’s disease, even before other clinical signs are fully apparent.:contentReference[oaicite:11]{index=11}
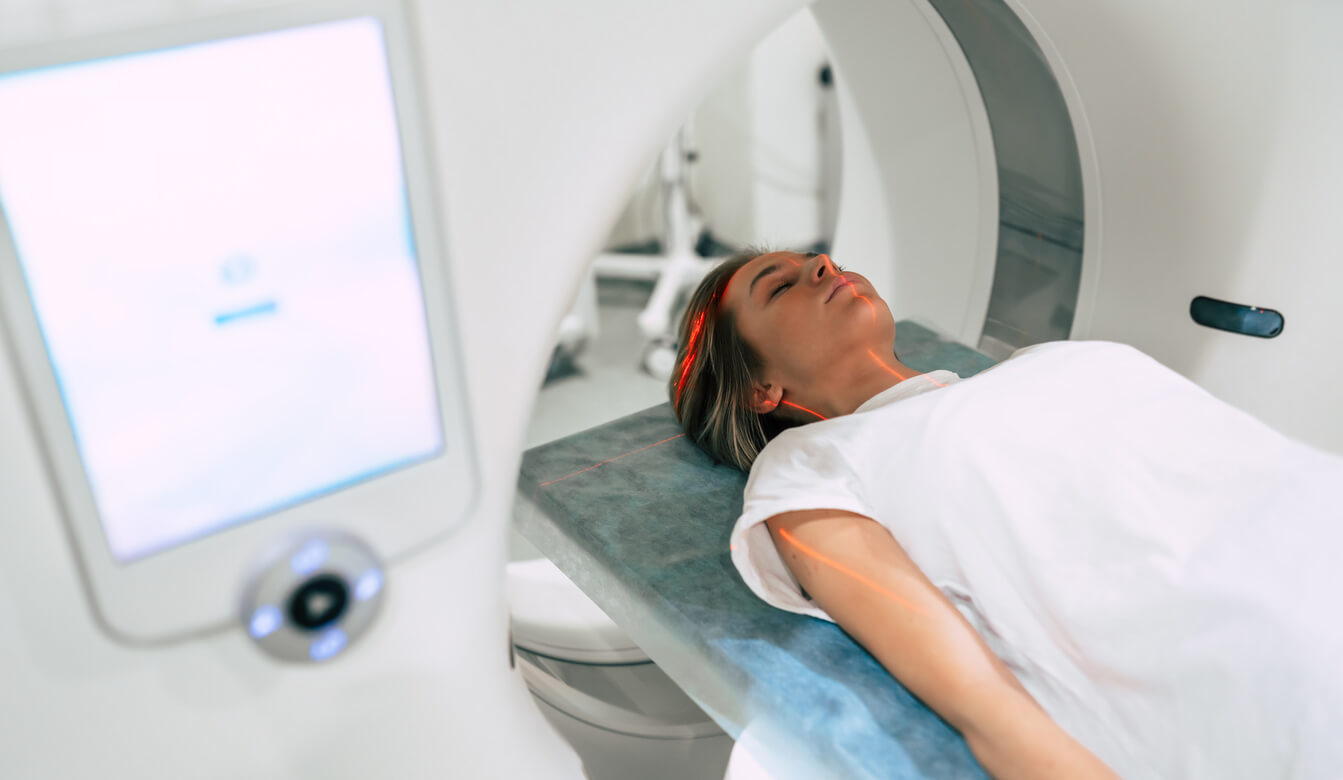
CT Scan
CT scanning provides detailed images of bony structures in the inner ear. It is useful for identifying structural abnormalities that may contribute to balance symptoms.
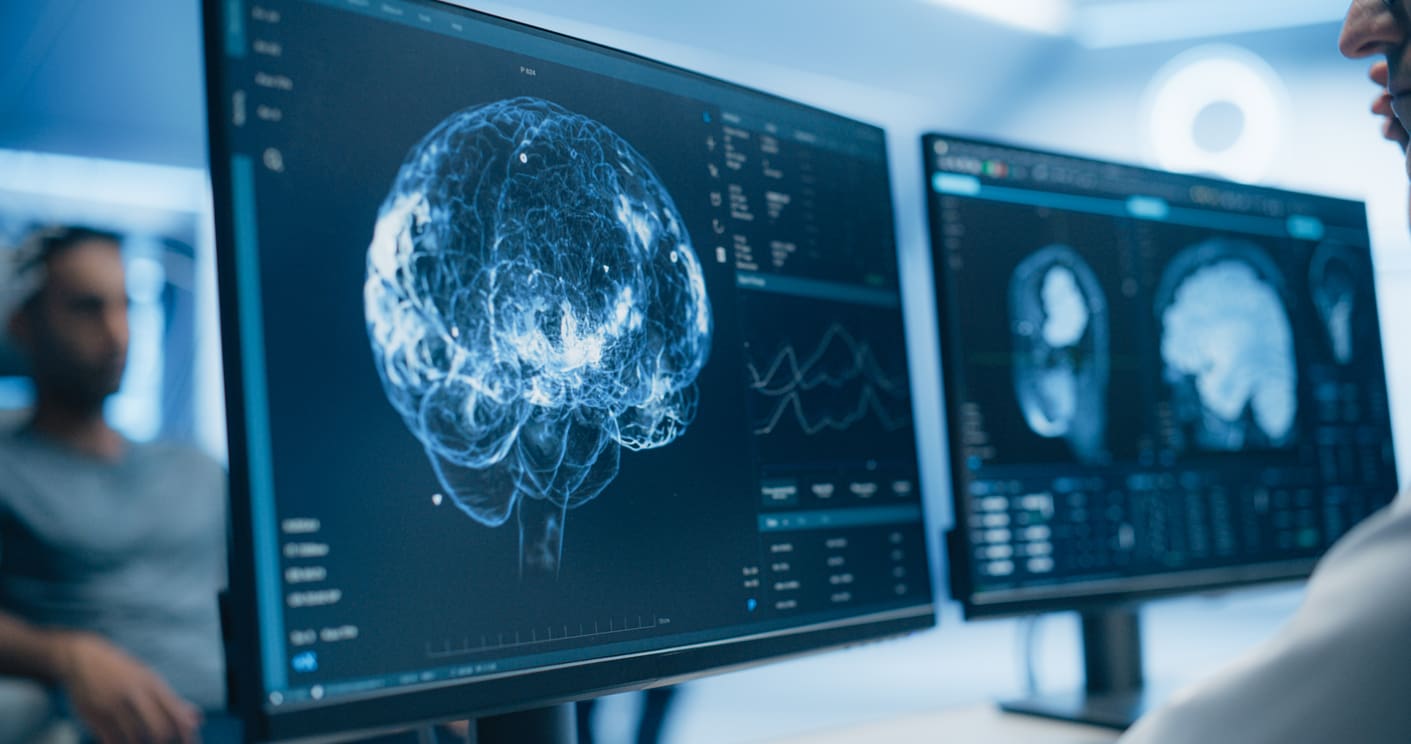
MRI Scan
MRI scanning provides high‑resolution images of nerves and soft tissues. It is used to exclude central causes of dizziness, such as acoustic neuroma, particularly when hearing loss is present.
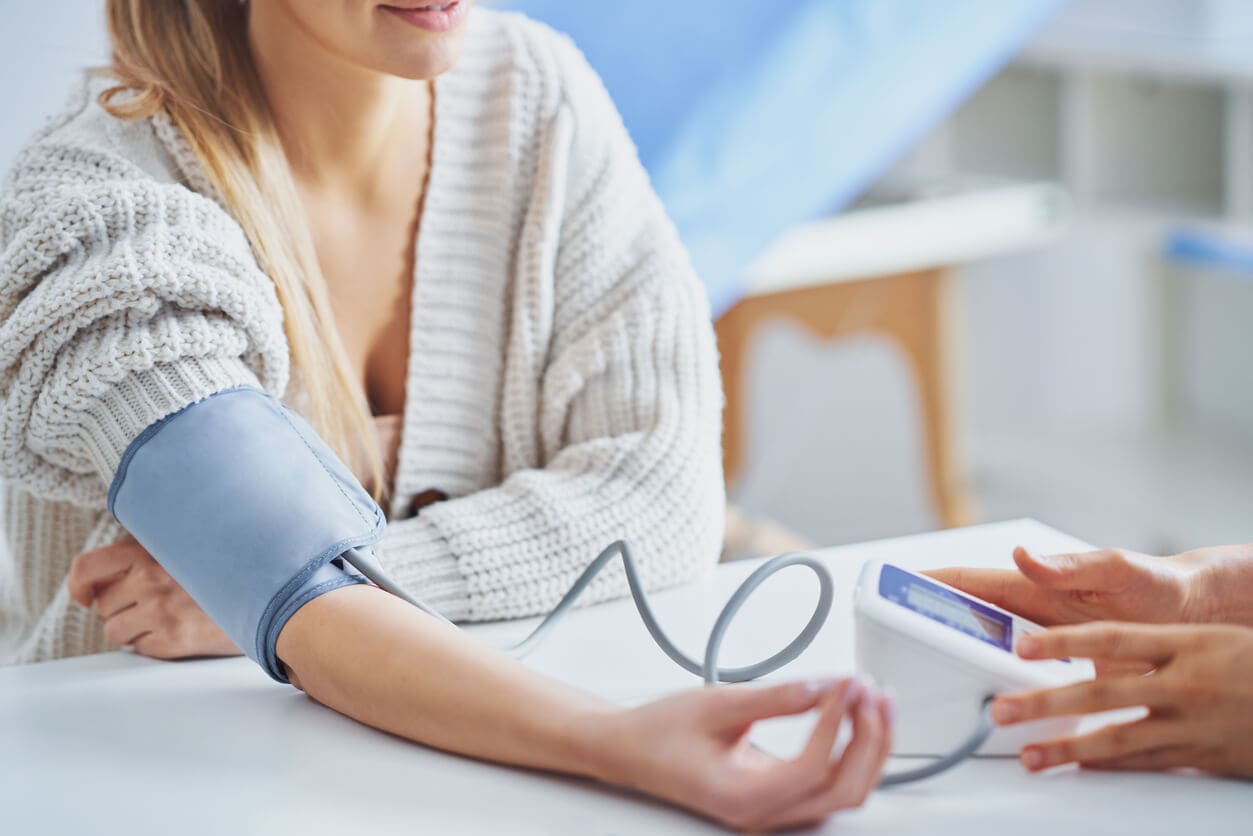

Blood Pressure
Blood pressure measurement may be included in balance testing to assess whether changes in circulation contribute to dizziness or light‑headedness. Standing and lying measurements help identify postural hypotension or autonomic dysfunction that can impact balance.:contentReference[oaicite:14]{index=14}
Blood Tests
Blood tests may be performed to exclude conditions such as anaemia or abnormal blood sugar levels that can cause light‑headedness or imbalance. A sample is taken by a practice nurse and sent for laboratory analysis to provide additional diagnostic information.:contentReference[oaicite:15]{index=15}
The private health insurances we work with
Harley Street ENT is recognised by a wide range of leading UK and international private health insurers, ensuring easy access to our care for patients with approved cover.

Need help and advice? Speak to an advisor
To discuss your needs in confidence or arrange a consultation, please contact our advisory team, who will be happy to assist you.







